Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations . Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon.
from www.radcliffecardiology.com
Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death.
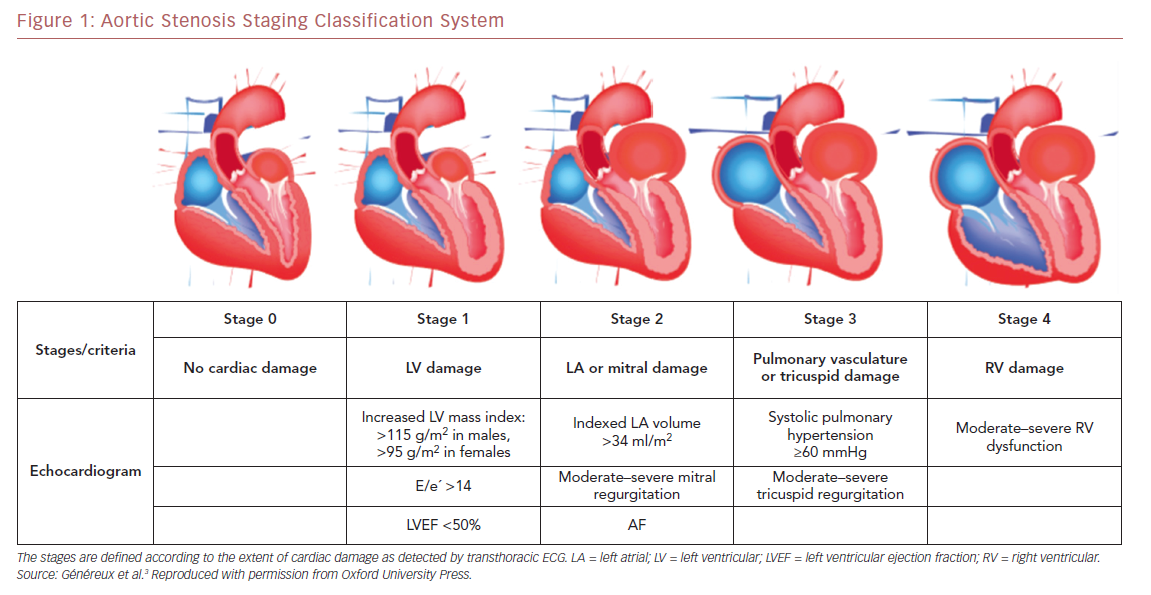
Aortic Stenosis Staging Classification System Radcliffe Cardiology
Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events.
From childrenheartcare.com
Management of Aortic Stenosis (AS) Dr. Gaurav Agrawal Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Relief of pulmonary stenosis. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.jcvaonline.com
Anesthetic Implications of Aneurysmal Main Pulmonary Artery and Left Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Restrictive respiratory. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.nysora.com
Aortic stenosis management NYSORA NYSORA Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From dokumen.tips
(PDF) Pulmonary Vein Stenosis Complicating Ablation for Atrial Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From mavink.com
Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Echo Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital.. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.bajajfinservhealth.in
Pulmonary Stenosis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From heart.bmj.com
Pulmonary stenosis update on diagnosis and therapeutic options Heart Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.jacc.org
Prognostic Implications of Moderate Aortic Stenosis in Patients With Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Anesthetic considerations in the patients of chronic obstructive Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Symptoms range from none. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From journals.lww.com
Infundibular Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia & Analgesia Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents,. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From aneskey.com
Chapter 31 Cardiac PressureVolume Loops Anesthesia Key Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.cardioguide.ca
Pulmonary Stenosis Cardio Guide Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.youtube.com
Anesthesia for Aortic Valve Surgery YouTube Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch pulmonary arteries. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.scribd.com
Pulmonary Stenosis PDF Heart Congenital Heart Defect Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. Symptoms range from none. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.vrogue.co
Anesthetic Considerations For Patients With Aortic Va vrogue.co Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by.. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.medicinekeys.com
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PS) Medicine Keys for MRCPs Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.openanesthesia.org
Aortic Stenosis Hemodynamic Management, Comorbidities, and Treatment Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Symptoms range from none to profound cyanosis and the potential for sudden death. Pulmonary stenosis is mostly congenital. Anaesthetic management of patients with severe pulmonary stenosis requires understanding of its physiological adaptations and also the events. Pulmonary stenosis is any obstruction within the rv outflow, at the pulmonary valve annulus or pulmonary valve leaflets, or within the main and branch. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.
From www.scribd.com
Anesthesia Considerations for a Patient with Mitral Stenosis Undergoing Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations Restrictive respiratory diseases are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized on pulmonary function tests by. The hemodynamic effects of ventilation strategies, positioning, pharmacological agents, and blood loss must all be considered to appropriately balance pulmonary and systemic blood. Relief of pulmonary stenosis is recommended for all patients with a peak gradient >/= 50 mm of hg and percutaneous pulmonary balloon.. Pulmonary Stenosis Anesthesia Considerations.